Premium is added to your mortgage. Tax is paid upfront.
What is mortgage default insurance?
Mortgage default insurance is a type of insurance that protects the lender if a borrower fails to repay their mortgage. In Canada, federally regulated lenders (Canadian banks) cannot offer a mortgage with more than 80% loan-to-value without mortgage default insurance backing it. This means that buyers who make a down payment of less than 20% of the home’s purchase price must pay for mortgage default insurance.
Who does mortgage default insurance protect?
Mortgage default insurance protects your lender if you default on your mortgage. The way this works is that, if you stop making your mortgage payments, your lender will foreclose on your home. The lender will then sell your home but, if they incur any losses while going through that process, the insurance policy will cover their losses. The insurance policy does not cover any losses that you as a homeowner might experience.
How to qualify for mortgage default insurance
In Canada, mortgage default insurance is sold by the Canadian Mortgage Housing Corporation (CMHC), as well as private insurers such as Sagen (formerly Genworth) and Canada Guaranty. Even though private insurers also offer default insurance, people commonly refer to it as ‘CMHC mortgage default insurance’. This is because CMHC accounts for roughly 60 % of the mortgage insurance market in Canada, making it the largest provider.
To get approved for mortgage default insurance, you must meet certain eligibility criteria. This includes having a minimum down payment of 5% for homes under $500,000 (with higher minimums for more expensive homes). You must also purchase an owner-occupied property, and maintain a sufficient credit score. The lender will also evaluate your Gross Debt Service (GDS) and Total Debt Service (TDS) ratios to ensure you can afford the mortgage. Federally regulated lenders will apply for the insurance on your behalf as part of the mortgage approval process.
How much does mortgage default insurance cost?
The cost of mortgage default insurance depends on the size of your down payment. The table below shows the CMHC rates for 2026.
CMHC Insurance Premium Rates
Primary Residence (Owner-Occupied)
Maximum LTV: 95%| Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio | Premium Rate | Example ($500k) |
|---|---|---|
| 90.01% – 95% | 4.00% | $18,501 |
| 85.01% – 90% | 3.10% | $13,563 |
| 80.01% – 85% | 2.80% | $11,551 |
| 75.01% – 80% | 2.40% | $9,301 |
| 65.01% – 75% | 1.70% | $5,950 |
| ≤ 65% | 0.60% | $975 |
Investment / Small Rental (Non-Owner Occupied)
Maximum LTV: 80% (Minimum 20% down payment)| Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio | Premium Rate | Example ($500k) |
|---|---|---|
| 75.01% – 80% | 2.90% | $11,238 |
| 65.01% – 75% | 2.00% | $7,001 |
| ≤ 65% | 1.45% | $2,356 |
For example, let’s say that you buy a townhouse worth $500,000 and you put a down just 5% of the purchase price. In this case, you will charged a rate of 4% of the loan value, which is $475,000 * 0.04 = $19,000. You must also pay tax Quebec Sales Tax (QST) on top of your insurance premium which is $2,240.63. The $19,000 gets added to your mortgage however, the $2,845.25 will get added to your closing costs and must be paid at closing.
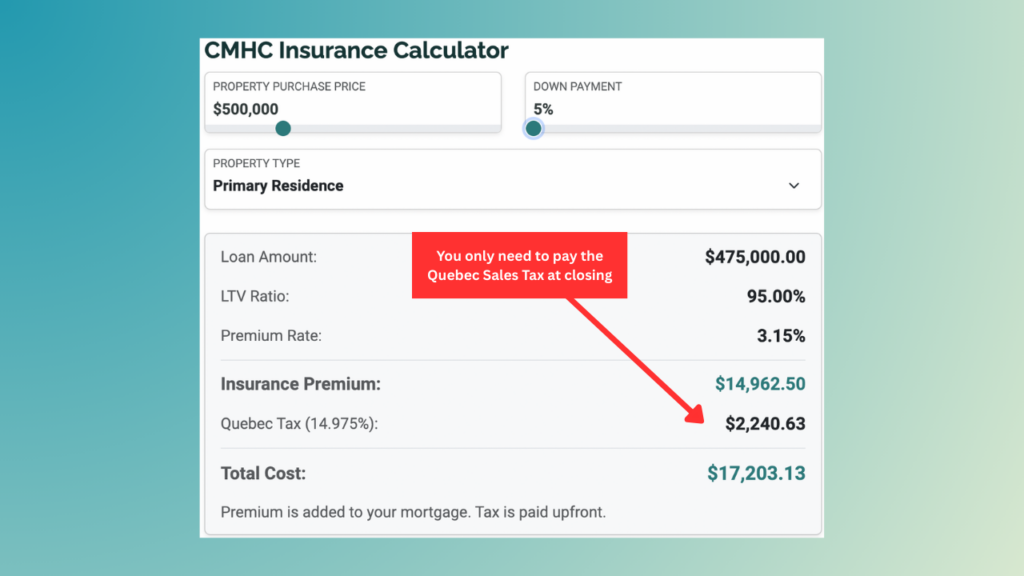
How do you pay for CMHC default insurance?
You do not need to pay for the entire cost of CMHC default insurance before buying your home. In fact, the only money you have to pay up front is the Quebec Sales Tax. The rest of the CMHC default insurance premium is added to your mortgage and you will pay interest on this. This does add a substantial amount of extra interest to your total cost of homeownership over the life of the mortgage however, in some cases it may be worth it.
For example, between 2020 and 2025, Montreal home prices almost doubled. In this case, the cost of delaying homeownership for many people in 2020, could have been higher than the extra interest paid on an insured mortgage.
Can you get a refund or a discount?
The CMHC does offer a partial refund of up to 25% if you purchased an eco friendly home or, if you make qualifying eco friendly upgrades to your home.
The reason for this is that the energy-efficient homes tend to have lower monthly utility costs and are more desirable. This lowers the risk of mortgage default by reducing the monthly costs that homeowners must bear and, at the same time, it increases the long-term value and marketability Canadian housing stock.
What If You Switch Homes? (CMHC Portability)
CMHC insurance is sometimes portable. This means that you can transfer it to a new property without paying a premium. This option applies if you buy a new home within a set period (usually six months to two years) and if your new mortgage does not exceed the balance of your previous mortgage. This helps you avoid paying twice for the same coverage. However, you should always check eligibility before making the move.
How to minimize mortgage default insurance
The only way to minimize your mortgage default insurance is to make a larger down payment. To do this, you will need to either save more money or ask for a gifted down payment. If saving more is your only option, start by using registered accounts such as the First Home Savings Account (FHSA) (in Quebec this is called CELIAPP) and the RRSP first home buyers plan. These can help you save significantly faster than using just a regular savings account.
>> Learn more about first time home buyer financial incentives in Quebec.
Final remarks
To approve your mortgage, federally regulated lenders require CMHC insurance if you put down less than 20%. This insurance is there to protect the lender in the case that you default. Whilst CMHC insurance is expensive, it can reduce your monthly interest rate compared to if you borrow money from a private lender without mortgage insurance. That said, CMHC default insurance increases the size of your mortgage and adds tens of thousands of dollars to the cost of your mortgage.
To see how mortgage default insurance affects your monthly payments, check out our mortgage cost calculator.













