When people talk about CMHC in Canada, they are normally talking about how it relates to mortgage insurance. This normally comes up when you are looking to put less than 20% down since CMHC insures you in the case of mortgage default.
However, the CMHC does a lot more than just insure home mortgages.
In this short article, we take a look at:
- What is the CMHC?
- How does the CMHC fulfil on its mandate?
- What is CMHC mortgage insurance?
- How is the CMHC funded?
What is the CMHC?
The CMHC is an acronym that stands for the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation. It is one of Canada’s federal Crown Corporations. It has the primary mandate of providing mortgage liquidity, assisting in establishing affordable housing development and providing arms length advice to the Canadian Government and housing industry.
How does the CMHC fulfil on its mandate?
At a high-level, CMHC fulfills its mandate through a combination of programs, tools, and policy actions. Many of these serve more than one goal simultaneously. Some examples of the ways in which the CMHC fulfil on its mandate include:
Mortgage insurance
Canadian residents are able to get a mortgage with as little as 5% down thanks to CMHC mortgage insurance. By insuring these high-ratio loans, CMHC reduces risk for lenders and encourages them to provide more mortgages. This helps to keep the housing market liquid and accessible.
Incentives & funding programs
CMHC offers programs like Eco Improvement and Affordable Housing Grants to encourage energy-efficient renovations and the development of affordable housing. These programs improve housing quality, increase supply, and make homes more accessible. They also indirectly support mortgage liquidity by encouraging homeowners to make value-adding improvements. This helps reduce the risk of loss in value on insured homes and thereby helps keep lenders offering mortgages.
Research, data & policy advice
CMHC conducts housing market research, collects and analyzes data, and provides policy advice to the federal government and industry stakeholders. This helps inform evidence-based decisions, improve housing programs, stabilize the mortgage market, and guide initiatives that ultimately improve the housing market across Canada.
What is CMHC mortgage insurance?
The Bank Act of Canada regulates how banks operate. This includes lending rules, capital requirements, and risk management. One key rule is that all high-ratio mortgages (loans with less than 20% down) must be insured. CMHC provides this insurance, which reduces lender risk and allows Canadians to buy homes with as little as 5% down, making homeownership more accessible.
To qualify for insurance, borrowers must meet income and debt limits, measured through the Gross Debt Service (GDS) and Total Debt Service (TDS) ratios. This insurance also allows banks to approve some buyers who might otherwise be rejected, expanding access to mortgages.
The main downside of CMHC insurance is that the premium is added to your mortgage. This means that the total amount that you will need to pay is higher than the purchase price. The cost of the insurance premium depends on both the purchase price and how much your down payment is. For example, if your mortgage is $475,000, and you put down 5%, then your insurance premium would be 4% of the purchase price (or $19,000). As your down payment increases, the insurance rate drops significantly. For instance, moving from 5% down to 10% down can almost halve the premium. The table below shows how the insurance percentage changes depending on your down payment.
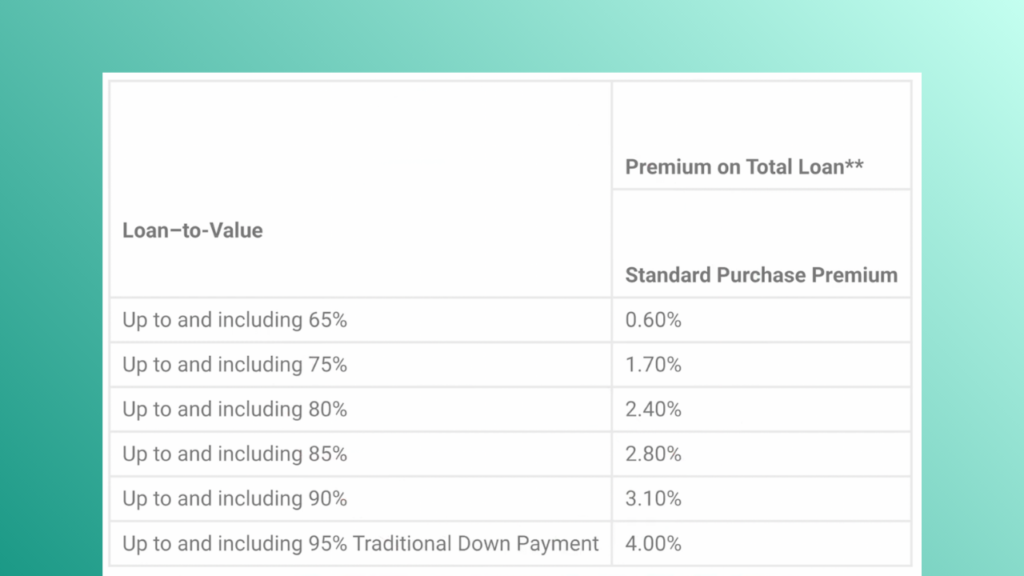
How is the CMHC funded?
The CMHC is funded through a mix of its own revenues and government backing. This depends on the program or activity. Here’s a breakdown of the primary sources of income for the CMHC.
- Insurance premiums (primary source of funding):
- The majority of CMHC’s funding comes from premiums paid by homeowners with CMHC-insured mortgages (usually when the down payment is less than 20%).
- These premiums cover operating costs, program expenses, and insurance claims.
- Government backing:
- CMHC’s mortgage insurance and some programs are backed by the federal government which reduces risk for lenders.
- While the government doesn’t fund day-to-day operations, it provides financial security and the ability to launch certain policy-driven programs.
- Program-Specific Funding:
- Some initiatives, like Eco Improvement or affordable housing programs, may involve targeted funding or incentives approved by the government.